Section 80GG is a tax deduction under the Indian Income Tax Act for individuals who pay rent but do not receive House Rent Allowance (HRA) from their employer.
Key Eligibility:
- You must be a salaried employee without HRA, self-employed, or a freelancer.
- You, your spouse, or minor child must not own a house in the city where you work.
- You must be paying rent for a residential property.
- Deduction Limit: The least of the following three amounts:
- Rs. 5,000 per month (Rs. 60,000 per year)
- 25% of your total annual income
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of your total income
- If your total annual rent exceeds Rs. 1,00,000, you must provide your landlord's PAN to claim the deduction.
Imagine that you have just secured your first job and are very excited to face this new stage of your life. You relocate to a new city, sensing great about the independence that comes with living alone. But as you get into the routine, reality starts hitting you with monthly expenses—rent being one of the biggest. Things can even get murkier: your employer does not grant a House Rent Allowance, thereby putting the burden of rent on you with no type of tax relief. You could have initially thought there was no way to lighten the load—maybe even feeling a little envious of colleagues who enjoy tax benefits from HRA.
But do not worry; there is one unsung hero in the tax code who can help people like you. Section 80GG of the Income Tax Act is the provision that comes to the rescue when HRA is absent in your salary slip. It is something like a superhero, where Section 80GG will save the day by reducing your taxable income and putting more money in your pocket. Be it a fresh graduate at the threshold of his career or someone who has spent quite a number of years managing without HRA, understanding this section may bring relief like salt to a wound.
Through the following article, we will break down Section 80GG into something simple and easy to understand, even if taxes always seem confusing.
What Is Section 80GG?
Section 80GG is a deduction you can claim for the rent you pay for your residential accommodation. It’s designed specifically for individuals who live in a rented house but do not receive a House Rent Allowance (HRA) from their employer. Maybe you're self-employed, a freelancer, or work for a company that doesn't provide an HRA component in your salary. This section is your answer.
But (and there's always a 'but' with tax rules, isn't there?), Section 80GG comes with its own set of rules and conditions. It’s not a free-for-all deduction, but when you qualify, it can make a real difference to your final tax outgo. The beauty of this section is its inclusivity. It doesn't matter if you're a salaried employee without HRA or a business owner, if you're paying rent for a place to live, you can potentially claim this benefit.
So, the next logical question is, who gets to unlock this benefit? The eligibility criteria are specific, but don't worry, we'll break them down in a way that's easy to understand.
Recent Updates
As of September 2025, there have been no changes to the provisions of Section 80GG of the Income Tax Act. The deduction remains available to individuals who do not receive House Rent Allowance (HRA) under Section 10(13A).
- Deduction Limit: The deduction is the least of the following:
- Rent paid minus 10% of total income.
- 25% of total income.
- Rs. 5,000 per month.
- Total Income: Calculated after deducting long-term capital gains, short-term capital gains under Section 111A, deductions under Sections 80C to 80U (excluding 80GG), and income under Section 115A.
- Mandatory Form: To claim this deduction, filing Form 10BA is mandatory. The acknowledgement number from Form 10BA must be entered in Schedule 80GG while filing the income tax return.
- Due Dates for Form 10BA Submission:
- For returns due by July 31, 2025: The deadline for submitting Form 10BA has been extended to September 16, 2025.
- For returns due by October 31, 2025: The deadline remains October 31, 2025.
Who Is Eligible For A Section 80GG Tax Deduction?
You must meet some requirements to qualify for claiming tax deductions under Section 80GG of the Income Tax Act, 1961. Here’s an analysis of who is eligible:
- Eligible Individuals: If you fall under the category of individuals and Hindu Undivided Families(HUFs), you qualify to claim deductions under Section 80GG. However, business and commercial organisations cannot benefit from this.
- Status of Employment: Salaried employees, as well as self-employed individuals can avail benefits of tax deductions under Section 80GG. Nevertheless, individuals with no income are ineligible irrespective of the rent paid by them.
- Form Requirement: A completely filled Form 10BA is submitted to the government to claim such deductions. This form acts as proof that you do not have a self-occupied property anywhere and claim benefits on that.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): Employees who do not receive HRA from their employers are eligible to claim these benefits. However, receiving HRA even for a month invalidates you for an entire fiscal year.
- Rent And PAN Card Requirements: If your years’ rent surpasses Rs. 1 lakh, then a PAN card belonging to the landlord of the property you are renting, is required.
- Living With Parents: You still qualify to claim deductions under Section 80GG even if you stay in a property owned by you parents. All you need is to sign a formal rental agreement with them and voila the rent is taxable in their hands.
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs): An NRI, if they rent a property in India, is eligible to avail these tax benefits.
Are you confused about how the calculation is done? Worry not! We are here to help you!
How Are Deductions Under Section 80GG Calculated?
Deduction under Section 80GG is allowed as the least of the three amounts:
|
Description
|
Calculation / Details
|
|
Determine the three possible deduction amounts (least of these will be allowed)
|
a) Maximum allowed under law: Rs. 5,000 per month or Rs. 60,000 per year
b) 25% of Adjusted Total Income
c) Rent paid minus 10% of Adjusted Total Income
|
|
Compute Adjusted Total Income
|
Start with overall income
- Subtract Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG)
- Subtract Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG) under Section 111A
- Subtract deductions under Sections 80C–80U (except 80GG)
- Subtract incomes taxed at special rates (Sections 115A, 115AB, 115AC, 115AD)
|
For instance,
Consider a taxpayer paying a monthly rent of Rs. 7,000, resulting in an annual rent of Rs. 84,000.
The adjusted Total Income of Rs. 3,00,000. The three amounts for Section 80GG deduction are:
- (a) the maximum limit of Rs. 60,000 per year,
- (b) 25% of the Adjusted Total Income, which is Rs. 75,000, and
- (c) the total rent paid minus 10% of the Adjusted Total Income
This is calculated as Rs. 84,000 - Rs. 30,000 = Rs. 54,000.
The deduction allowed under Section 80GG is the least of these amounts, so in this example, the taxpayer can claim Rs. 54,000.
Which Property Owners Can Benefit From Tax Deductions
There are two major requirements that a property owner must adhere to in order to avail of the tax deductions allowed under Section 80GG. These are as follows:
- Payment of Rent for Present Residence: The property owner has to pay rent for the property in which he is currently residing. Section 80GG benefits are applicable only when a taxpayer is not staying in his own property and is instead living on rent.
- Property Location Requirement: The property or properties owned must not be located in the same city or area where the taxpayer's place of work is situated. If the property is owned by a taxpayer in the city where they work but chooses to stay in a rented property, Section 80GG is not applicable.
However, if the property owned lies in some other city or any other location, then it will be "let out," and the assessee can claim the benefits of Section 80GG for the rent paid in the current city of residence.
Pros And Cons Of Section 80GG
Let’s understand a few advantages and disadvantages of claiming deductions under Section 80GG.
Pros
There are a number of benefits granted under Section 80GG, especially to a person paying rent for their accommodation without receiving House Rent Allowance (HRA).
- Reduced Tax For Rent Payments: Section 80GG allows an individual to claim a tax deduction related to the housing rent paid when they do not receive HRA from their employers, as in the case of self-employed workers, low-income earners, or those in early career stages.
- Wider Eligibility: This section applies to both salaried and self-employed individuals. The applicability of this section places a larger portion of taxpayers, including those with minimal or no income, at an advantage for a reduction in tax liability.
- Lower Tax Liability: Under Section 80GG, when deductions are claimed by various individuals, there will be an effective reduction in tax liability. This ultimately leads to filing less tax and helps in better managing the finances of an individual.
Cons
Section 80GG does come with certain disadvantages:
- The amount for deduction is limited: The maximum deduction allowed under Sec 80GG is Rs. 2,000 per month or 25% of the total income, whichever is lower. This might translate to small savings in tax if someone has a higher income or pays high rent.
- Rent threshold requirement: For this deduction, the amount of rent paid must be more than 10% of the total income. It thus follows that in the case of people who pay low rents or have comparatively high incomes, this benefit cannot be availed of, which makes this section of less utility to such taxpayers.
- Exclusion in Case of Claim: Any person claiming a deduction under Section 80GG is not allowed to claim tax rebates available under other sections on the same rent paid. This exclusivity can narrow down the aggregate tax benefits accruable to all persons who pay rent.
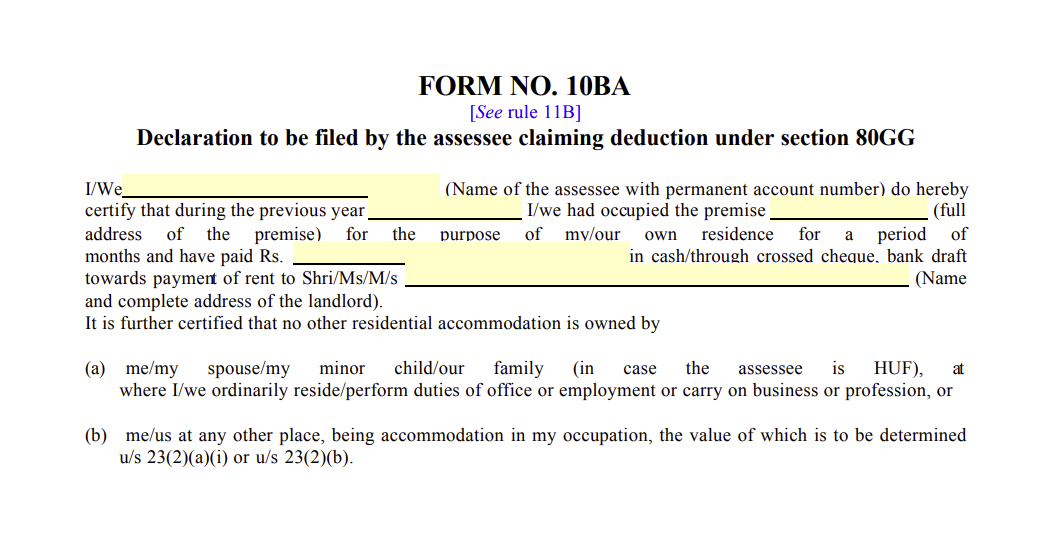
How To Fill Form 10BA?
Form 10BA is an essential element while claiming tax advantages under Section 80GG. The following details are required while filling out the form:
- A complete address and postal code for the rented property are needed.
- The full name and the Permanent Account Number (PAN) of the individual claiming tax deductions must be provided.
- Configure how the rent is paid, such as through bank transfer, cash or any other mode.
- Mention the duration of your stay on the rented property in months.
- The name and address of the property owner should also be mentioned.
- You need to ascertain that neither you, your spouse, nor your minor child have any residential property under their name.
- If the total rent exceeds Rs. 1 lakh, then the landlord's PAN must be provided as well.
Source: https://img.indiafilings.com/learn/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/12004022/Form-10BA.png
How To Claim Deduction Under Section 80GG?
Here’s a stepwise guide to help you through the process of claiming a deduction under Section 80GG:
- Personal Information: Provide your personal details like full name and your PAN details.
- Lease information: Details about the address of the property with the postal code is needed. Also, the duration of your stay on the property and how the rent is paid must also be mentioned.
- Details of the property owner: The name and address of the landlord need to be provided.
- Declaration: On Form 10BA, declare that neither you nor your spouse nor your minor child nor the HUF of which you are a member owns any residential property.
Documents Required For The Claim Deduction Under Section 80GG
The below-mentioned documents are required:
- Rent Receipts: Rent receipts throughout the financial year should be collected. Each receipt should have the following details:
- The full name and address of the property owner.
- The rent payment.
- The duration of rent payment.
- If possible, a revenue stamp.
- Make sure the rent slips for every month are available.
- Rent Agreement: A copy of the lease agreement would act as additional proof of your stay on the rented property. Although not compulsory, it is an added factor in case tax authorities need it.
- Declaration In Form 10BA: Form 10BA is submitted to declare your claim deductions under Section 80GG. In case your rent exceeds Rs. 1 lakh, this form becomes a compulsion.
- PAN Of The Landlord: Under circumstances where your rent paid is more than Rs. 1 lakh, it is necessary to provide the PAN of your landlord.
- Other Supporting Documents: Though not necessary, additional documents like bank statements or cancelled cheques proving rent paid to your property owner can always come in handy.
80GG vs HRA
So, you're paying rent and you want to save on taxes. That's smart! But now you might be wondering, "I've heard of HRA, and now 80GG... which one is for me?"
It’s a great question. Think of it like this: HRA (House Rent Allowance) and Section 80GG are two different doors to the same room - tax savings. But you can only walk through one door. You don't get to claim both for the same rent payment. The choice isn't yours to make randomly, though. It’s decided by a very simple factor: your salary slip.
Let's break it down with a simple table:
|
Feature
|
House Rent Allowance (HRA)
|
Section 80GG
|
|
Who Can Claim?
|
Salaried employees who receive HRA as a part of their salary.
|
Anyone who pays rent but does not receive HRA. This includes self-employed individuals, freelancers, and salaried employees without an HRA component.
|
|
The "Source" of Benefit
|
It's an allowance from your employer. You get an exemption on it.
|
It's a deduction you claim from your Gross Total Income.
|
|
Most Important Rule
|
You must have HRA mentioned in your salary structure to claim it.
|
You must NOT be receiving HRA from your current employer to claim this.
|
|
Simplest Way to Decide
|
Look at your salary slip. Is there an HRA component? If yes, claim HRA. It's almost always more beneficial.
|
Look at your salary slip. Is there no HRA component? If it's blank, Section 80GG is your go-to option.
|
So, if your salary includes HRA, you claim HRA. It's that simple. Section 80GG is your dedicated backup plan, your special tax-saving instrument for when the main HRA benefit isn't available to you. It ensures you don't miss out just because your income structure is different.
80GG vs Other Sections
Now, you might be thinking, "Okay, but how does 80GG fit in with all the other deductions I claim?" Managing your taxes is like assembling a toolkit, you use the right tool for the right job.
The best thing about the Income Tax Act is that most deductions can coexist peacefully. Claiming one doesn't usually block you from claiming another, as long as you meet the individual criteria for each.
Here’s a quick comparison to show you how 80GG plays with others:
- Vs. Section 80C: Investments in ELSS, life insurance premiums (like the robust plans we offer at SMC Insurance), PPF, etc. Section 80GG is completely separate. You can claim the full deduction under 80C (up to Rs. 1.5 Lakh) and then also claim your eligible deduction under 80GG. They are teammates, not competitors.
- Vs. Section 80D: This is for the premiums you pay for health insurance for yourself and your family. Again, it’s a different category. Paying rent doesn't affect your health insurance claims. You can comfortably claim both 80D and 80GG, building a strong shield for both your health and your wallet.
- Vs. Section 80TTB: This section is specific to interest income from banks and post offices for senior citizens. It has no direct connection to rental payments. A senior citizen who is paying rent and not receiving HRA can absolutely claim both 80TTB on their interest income and 80GG for their rent. The law specifically allows for this.
Special Cases
Life isn't always straightforward, and neither are our living arrangements. You might be wondering, "This all sounds great, but what about my specific situation?" Let's walk through some common but tricky scenarios. The rules are specific, but don't worry, we'll make sense of them together.
- What if I'm an NRI?
This is a big one. If you are a Non-Resident Indian (NRI) for tax purposes, here's the crucial detail: You cannot claim a deduction under Section 80GG. The law is clear that this benefit is available only to Resident Individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs). So, if your income is classified as Non-Resident in a given financial year, this particular door to tax savings remains closed. But it's always wise to consult a tax expert to understand other avenues available to you.
- What if I Own a Home in Another City?
This is a common situation in today's mobile workforce. Imagine you own a house in your hometown, but your job requires you to live and pay rent in Mumbai, Delhi, or Bangalore. The good news? You are still eligible to claim Section 80GG.
There's a catch, of course. The law states that neither you, nor your spouse, nor your minor child should own a residential property in the city where you perform your office duties or business. So, owning a house in your hometown doesn't affect your claim for rent paid in your work city. You just have to ensure you don't own the roof over your head in the city where you are claiming the rent deduction.
- Can I Pay Rent to My Parents and Claim 80GG?
The short answer is yes, you absolutely can. This can be a legitimate way to channel funds within the family and save on tax. But, it has to be a genuine rental arrangement. You can't just write a rent cheque to your parents and call it a day. To stand up to scrutiny from the tax department, you need:
- A proper rent agreement on stamp paper.
- Your parents must declare this rental income in their ITR and pay the applicable tax on it.
- The rent amount should be justifiable and not overly inflated for the property's location and amenities.
If done correctly, it's a win-win. You get your tax deduction, and your parents earn a rental income. It’s a smart financial move, as long as everything is transparent and above board.
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Notices
Let's be honest, the thought of getting a notice from the Income Tax Department can make anyone a little anxious. The goal of claiming a deduction is to save money, not to invite trouble. So, let's talk about the common pitfalls people stumble into with Section 80GG and how you can steer clear of them.
|
Mistake
|
Explanation
|
|
Mistake #1: Inflating the Rent Amount
|
It can be tempting to show a higher rent to get a bigger deduction. But this is the fastest way to get a red flag. The tax department has a good idea of reasonable rental values in different areas. If your claimed rent seems unrealistically high for the type and location of your accommodation, you might be asked to explain.
Hence, always pay and declare the actual, fair-market rent. Keep all your bank statements or cheque records as solid proof.
|
|
Mistake #2: Not Having Proper Proof (Or Any Proof)
|
Your word alone isn't enough. Simply claiming the deduction without the documents to back it up is a huge risk. The most basic proof? Your rent receipts.
Thus, get a rent receipt for every payment. Make sure it contains:
- Your landlord's name and address.
- Your name as the tenant.
- The rental period and the amount paid.
- The landlord's signature.
In some cases, you may also need to provide your landlord's PAN card. If your total annual rent exceeds Rs. 1,00,000, providing your landlord's PAN is mandatory.
|
|
Mistake #3: Claiming 80GG While Receiving HRA
|
If your salary slip shows an HRA component, you must claim the HRA exemption. Claiming 80GG on top of that will certainly lead to a notice and a demand for extra tax.
Therefore, be honest when filing your return. Cross-check your Form 16 (which shows your HRA exemption) with your own calculations to ensure consistency.
|
Let’s Wrap It Up!
Section 80GG is a helpful tax provision for those paying rent but do not receive HRA from their employer. The deduction under this helps a lot in saving taxes and, hence, is a very practical tool for better management of finances. Though the benefits may sound modest, especially for those earning at higher rates, the relief it offers can be substantial for many taxpayers. It is essential to clearly understand the eligibility criteria and the methods of calculation so that you can provide a maximum deduction. Therefore, keeping all the documents and fulfilling all the requirements is very important so that you can claim this deduction without hassle and in the most effective way.
Want to know more about other sections of The Income Tax Act? Check out Section 206AB Of Income Tax Act and Section 115BAA Of Income Tax Act to learn more.